A lesson about the benefits and limitations of genetic engineering.
Simple, straightforward information about the coronavirus epidemic.
The most characteristic symptom of malaria is fever. The pathogen of the disease is spread by mosquitoes.
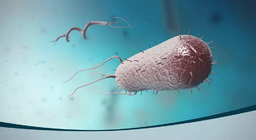
This lesson presents the structure and classification of bacteria and the role they play in our lives.
In this lesson, you can learn about the history, structure and use of optical microscopes.
Bacteria occur in a wide range of shapes, including spheres, rods and spirals.
Eukaryotic cells contain a number of organelles.
Mitosis is the process by which a eukaryotic cell divides into two cells, and the number of chromosomes remains unchanged.
Our gametes are haploid cells produced from diploid cells by meiosis, a special type of cell division.
This animation explains active and passive transport processes occurring through cell membranes
Bacteria are unicellular organisms that have no nuclei and are a few micrometres in length.
NAD⁺ is a coenzyme that plays an important role mainly in catabolic processes, while NADP is important in anabolic processes as hydrogen carriers.
Chlorophyll is a photosensitive green pigment found in plants; it absorbs light energy, thus plays a vital role in photosynthesis.
Enzymes are protein molecules catalysing biochemical reactions. Their activity can be regulated.
There are two basic cell types: prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells.
Typical plant and animal cells exhibit a number of similarities and differences.
Viruses consist of protein and DNA or RNA; they reprogram infected cells to produce more viruses.
An acyl-carrier coenzyme taking part in both anabolic and catabolic processes.
Genome editing is a type of genetic engineering which results in changes in the genome of an organism. This animation presents one of the best-known genome editing protocols, the CRISPR/Cas9 system.